Compiler Toolchains
Contents
Compiler Toolchain
The compiler toolchain is used to allow Flowcode to compile the generated C code into a binary file that can be executed on your target microcontroller device.
The "Compile to Hex" and "Compile to Target" options in Flowcode require that a toolchain is installed for your selected microcontroller device.
Downloading and installing toolchain
Most of the toolchains can be found here on the main Flowcode download page.
Download and run the toolchain installation file and that will do everything required to allow Flowcode to compile to that range of target devices.
Note if you have Flowcode open when installing the toolchain then you may need to restart Flowcode once the toolchain is installed.
ESP32 Toolchain
The ESP32 toolchain includes a lot more extras and so we have used the standard Espresif installer as that does all the extra functionality for you.
The only downside to this is you have to manually point Flowcode at the toolchain.
The toolchain can be downloaded from here: https://flowcode.co.uk/download
Please report any problems or issues on the Flowcode user forum.
Installation
Once the download has finished run the installation file.
Select – I accept the agreement and click Next
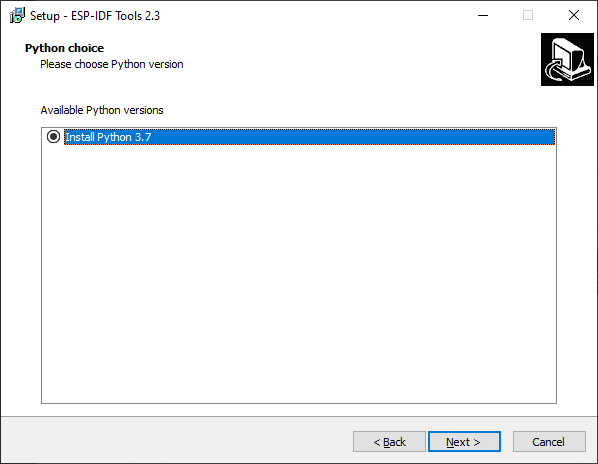
If you have Python already installed then you can select your version of Python.
Otherwise, select Install Python 3.7
Please note some versions of Python may cause the installer to fail, if this happens then try again and use the supplied version 3.7
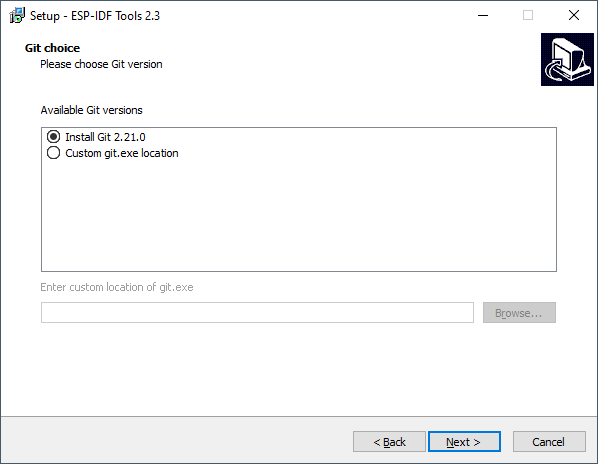
If you have Git already installed then you can select your version of Git.
Otherwise select Install Git
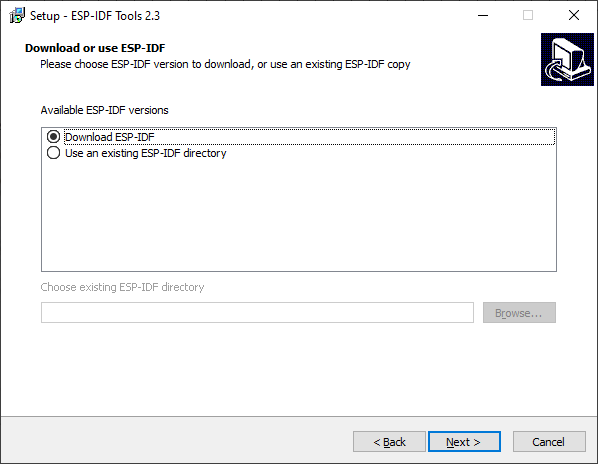
If you have an ESP-IDF already downloaded then you can select your version of ESP-IDF.
Otherwise, select Download ESP-IDF
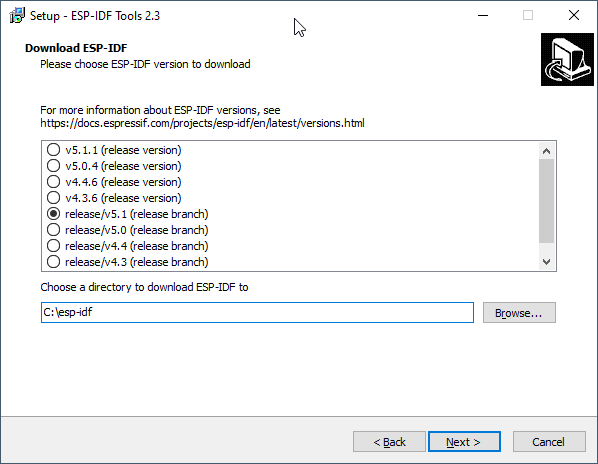
Select which ESP-IDF to install, we recommend the lowest version as the higher versions have not been tested.
At the time of writing 4.2 (Release branch is OK to use)
Edit: Currently the earliest version available to install is now 4.3.
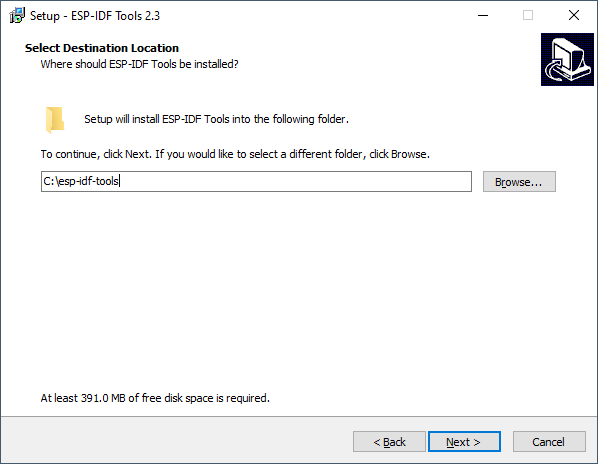
Install to a location on your system with no spaces in the path.
For example C:\esp-idf
Select a location for the ESP-IDF Tools to be installed, again use a path that contains no spaces
For example C:\esp-idf-tools
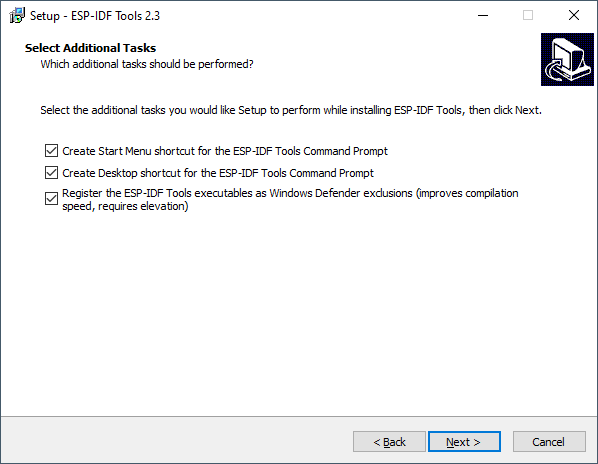
Select addition tasks, recommend keeping all options checked and click Next.
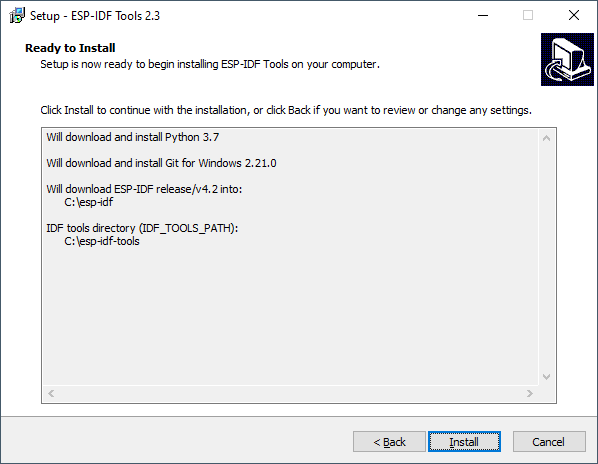
On the confirmation screen check the paths are correct and click Install
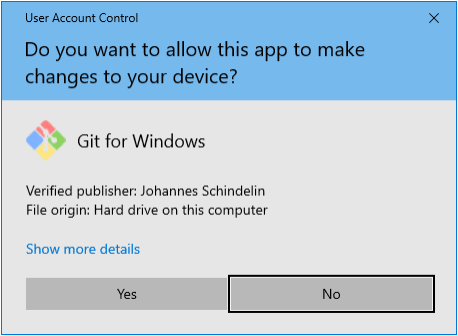
During the installation process you may get some of the following pop-ups appearing
Click Yes to allow Git to be installed
Click Yes to allow Windows PowerShell to be installed
Installation complete
You do not need to run the ESP-IDF command prompt as we will be invoking this from Flowcode:
A PC reboot may be required after installation has been completed.
Setting up Flowcode for use with the ESP32 toolchain
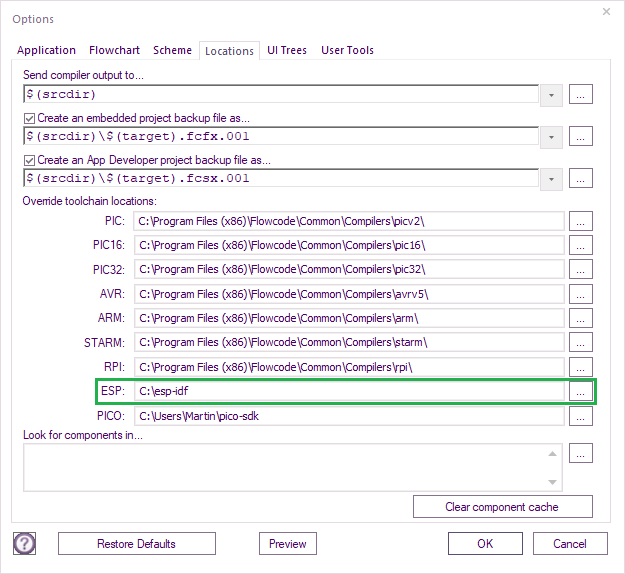
Copy the location of the esp-idf (e.g. C:\esp-idf) into the
Global Settings > Locations tab.
Or if you have a project loaded
File > Global Settings > Locations tab:
Click OK
Flowcode ESP32 Projects
When you create a new Flowcode ESP32 project the first time you compile a folder will be created in the Flowcode project directory with the same name as the Flowcde project file.
The folder contains all the standard build output for an ESP32 project.
The first compilation of a project will take a while to complete – around 5 minutes as all of the ESP32 libraries are pulled in from the ESP-IDF and compiled one by one. After the initial compilation subsequent compilations will be much faster.
Inside the folder is a file called sdkconfig, this file is a text file that contains the configuration for the ESP32 device.
Any changes to this file will automatically trigger another extended compilation.
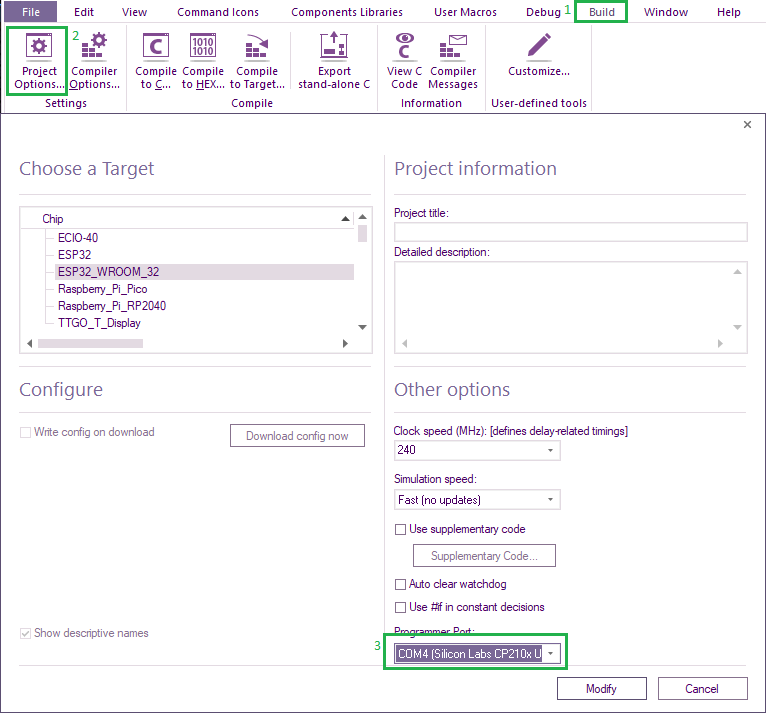
If you connect your ESP board before running Flowcode then the boards COM port will appear in the Flowcode project options.
This will need to be selected and correct for the Compile to Chip menu option to function correctly.
Pico Toolchain
Note: Using Raspberry Pi Pico with Windows 7 or 8 is not officially supported. To build Pico projects you will need to install the following tools:
ARM GCC compiler CMake Build Tools for Visual Studio 2019 Python 3 Git
Installing ARM GCC Compiler
Download the Windows Installer from:
https://developer.arm.com/downloads/-/gnu-rm
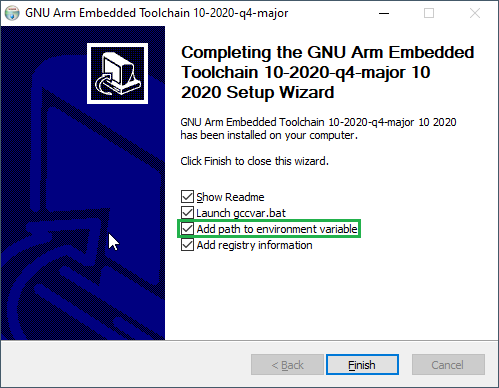
During installation, you should tick the box to register the path to the ARM compiler as an environment variable in the Windows shell:
The command prompt that the installation opened can be closed.
Installing CMake
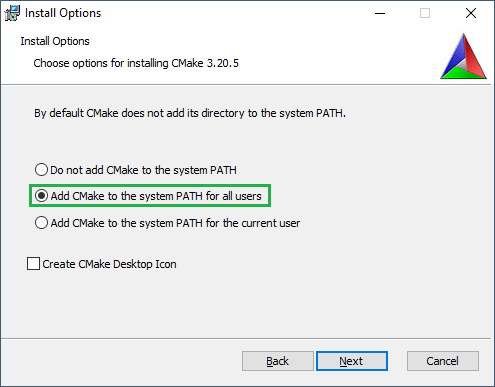
Download the Windows CMake3.20.5 Installer from: https://cmake.org/files/v3.20/
During the installation add CMake to the system PATH for all users:
A PC reboot is recommended after installing CMake.
Installing Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022
Download the Windows Installer from:
https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vs_BuildTools.exe
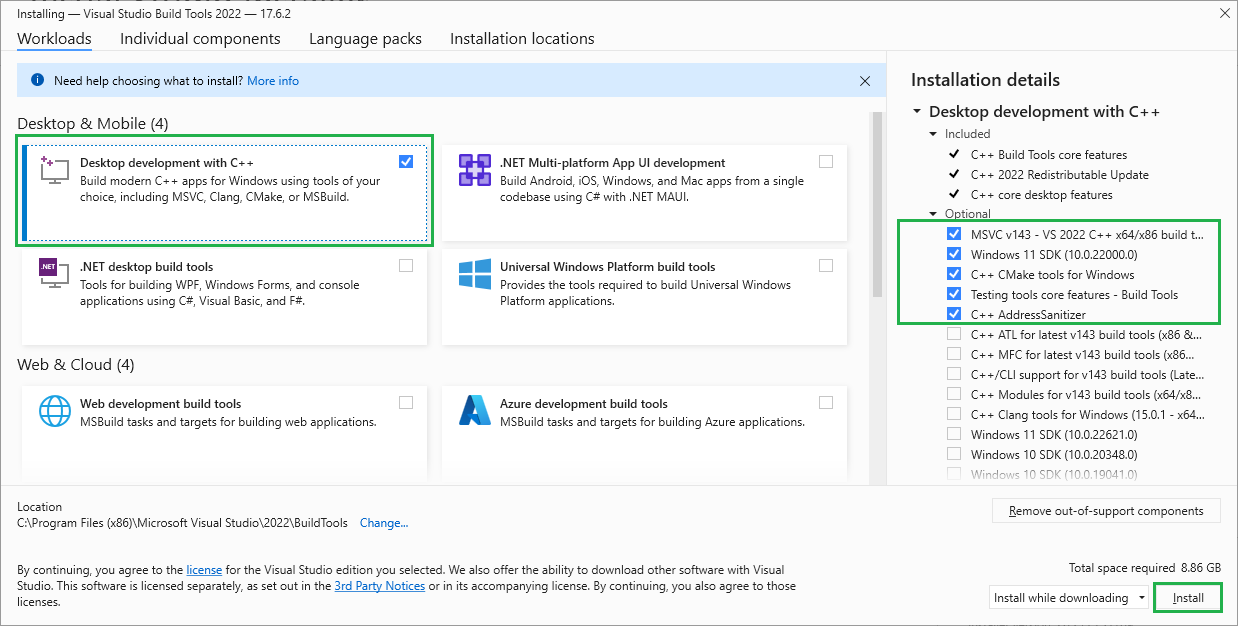
When prompted by the Build Tools for Visual Studio installer you need to install the C++ build
tools only.
You must install the full "Windows 10 SDK" package and leave the path as the default value:
At around 21% completed its takes a little while to continue, this is normal
Installing Python 3
If you already have Python 3 installed on your PC (for example if you have already installed the ESP toolchain) skip this section and do not re-install Python.
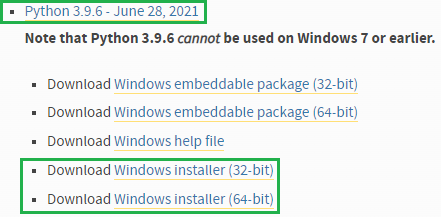
Download Windows Installer from: https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
Look for version 3.9.6:
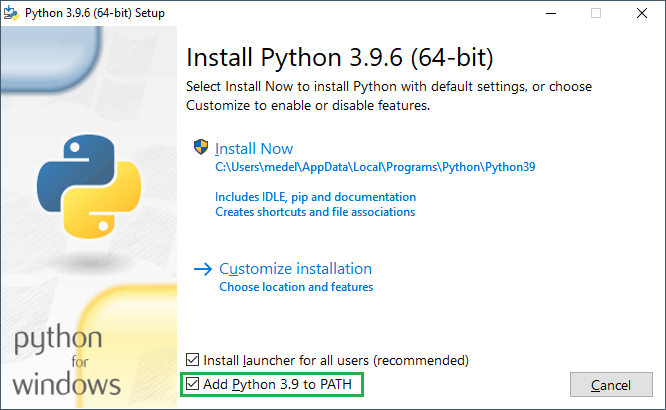
Ensure that it’s installed 'for all users' and add Python 3.9 to the system PATH:
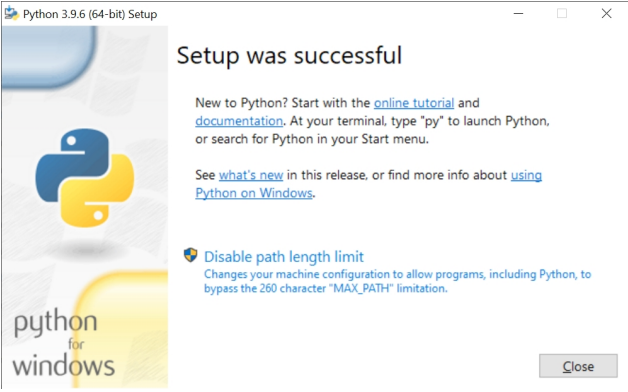
Disable the MAX_PATH length limit when prompted at the end of the Python installation:
Installing Git
Download the Windows Installer from: https://git-scm.com/download/win
When installing Git you should have Only show new options unselected.
There is no need to change any default setting for all the checkboxes
Ensure that you change the default editor away from vim, for example if you have notepad++:
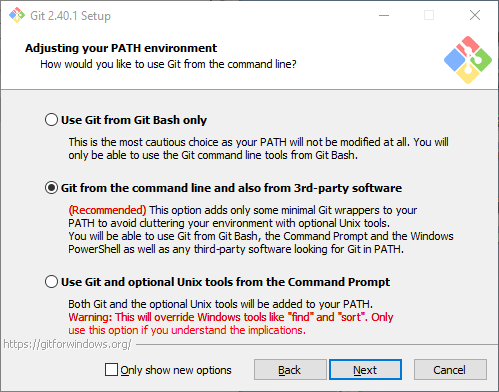
Ensure you tick the checkbox to allow Git to be used from third-party tools:
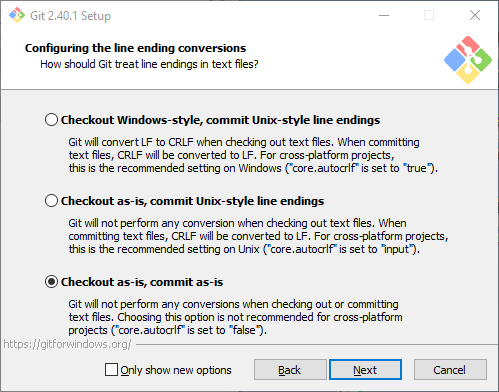
Don't select any NEW! options, leave options as default. Select "Checkout as is, commit as-is":
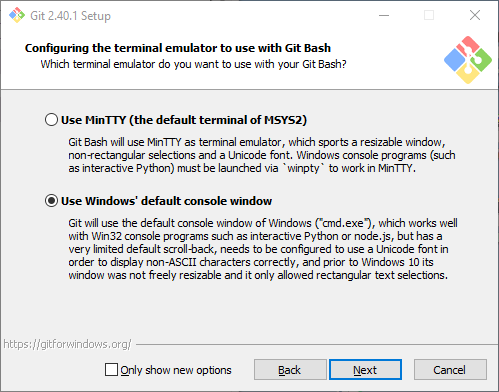
Select "Use Windows' default console window":
Leave all the defaults Ticked
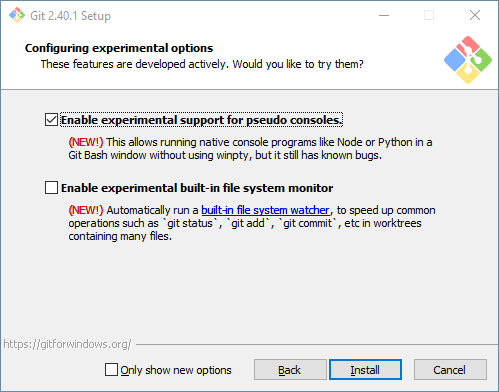
Check "Enable experimental support for pseudo consoles" during the installation process:
Installing the Pico SDK
Use Git to download the Pico SDK to a location on your PC.
For example, install to your user Downloads directory:
C:\Users\YourName\Downloads\pico-sdk
Run a command prompt (type "cmd" at the start search box) and run the following commands: cd Downloads
git clone -b master https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk.git
cd pico-sdk
git submodule update --init
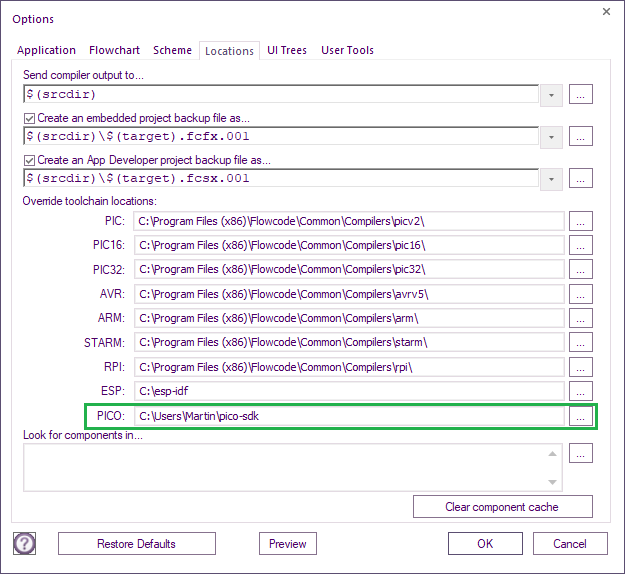
Setting up Flowcode for use with the Pico toolchain Copy the location of the Pico sdk (e.g. C:\Users\YourName\Downloads\pico-sdk) into the
Global Settings > Locations tab or if you have a project loaded
File > Global Settings > Locations tab:
Programming The Pico
The Pico is a free target device.
Run Flowcode & Select New Project
Either right-click on any target & select Search... and enter pico, then select Find Next:
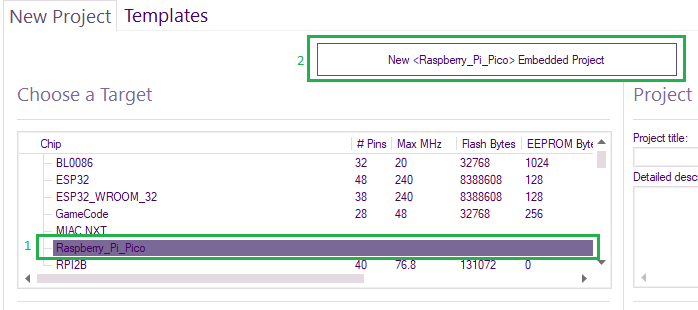
Or Go to the Free targets section, expand Free targets and scroll down and select Raspberry_Pi_Pico
Select New <Raspberry_Pi_Pico> Embedded Project:
Sending Your First Program
Before sending your flowchart to the Pico, you must first enable boot mode.
To do that, make sure the pico is not connected to your PC.
Hold the BOOTSEL down and plug the Pico into your PC.
If you hear the USB connected sound and you also get a popup like this:
Then your Pico is ready to be programmed.